CRM and CNRS researchers introduce a novel concept, Late Warning Signals (LWS), for aiding post-tipping point ecosystem recovery, enhancing resilience in biodiversity management. LWS may offer crucial insights for timely intervention in ecosystem dynamics, potentially revolutionizing conservation strategies.
Scientists are perennially aware that it is best not to trust theory until it is confirmed by evidence. It is equally true . . . that it is best not to put too much faith in facts until they have been confirmed by theory.
Robert MacArthur (Geographical Ecology, 1972)
Conservation Biology is at the forefront of efforts to understand and protect Earth’s ecosystems and biodiversity from threats that erode biotic interactions and lead to extinctions. With the goal of developing research and providing tools for preserving biodiversity and promoting sustainable ecological management, researchers Josep Sardanyés and Filip Ivančić, from the Centre de Recerca Matemàtica (CRM), along with Blai Vidiella, who was affiliated with the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE) at the time of the research and is now with the Station d’Écologie Théorique et Expérimentale (CNRS), have delved into the complexities of ecological dynamics to introduce a novel concept—late warning signals (LWS)—in their recent publication in the journal Biological Conservation. Their article is part of a special Issue about Non-equilibrium perspectives in biological conservation (edited by Sonia Kefi, Pierre Gaüzère, and Daniel Oro).Central to this exploration is the recognition of regime shifts—sudden, often irreversible alterations in the structure and function of ecosystems—that can be triggered by tipping points. These tipping points represent critical thresholds in the system’s behaviour, beyond which small changes can lead to large and often unforeseen consequences.
Ecosystems, despite their resilience and adaptability, are susceptible to abrupt regime shifts driven by tipping points, especially under the scenario of global change; even efforts to reduce or eliminate stressors that trigger these tipping points may not guarantee a return to their previous states. This highlights the importance of understanding not only the factors that lead to regime shifts but also the dynamics that govern the system’s recovery or potential collapse. To effectively mitigate the impacts of tipping points, conservation policies must incorporate monitoring mechanisms to track the indicators of ecosystems’ resilience, allowing for timely intervention and adaptive management strategies.
The research team’s investigation focuses on unravelling the complexities of ecological regime shifts triggered by tipping points in real ecosystems by means of theoretical and computational research. By studying these phenomena, they aim to bridge the gap between theoretical ecology and conservation practice, translating abstract concepts into tangible strategies for ecosystem management and restoration. Furthermore, the team examines how the properties of tipping points, such as hysteresis and resilience, influence ecosystems’ conservation, management, and restoration efforts.
“In our contribution, we discuss the critical transitions (CTs) that ecosystems undergo, emphasizing the need to identify warning signals indicating the approach of tipping points (so-called early warning signals), and especially those signals emerging after a tipping point has occurred” explains lead author Josep Sardanyés (CRM). “These signals are crucial for detecting the potential collapse or recovery of ecosystems.”
Introducing Late Warning Signals: new strategies for ecosystem recovery
One key innovation introduced in the study is the concept of late warning signals (LWS). Unlike early warning signals (EWS) that indicate an approaching tipping point, LWS provide evidence that a tipping point has already been surpassed, but the system remains in a transient state, offering a window of opportunity for recovery efforts.
“We provide evidence of late warning signals as a means to identify when a system has crossed a tipping point, yet the systems typically remain in a long transient state opening the possibility to take actions to avoid the collapse. This concept opens new avenues for conservation strategies aimed at restoring ecosystems even after critical transitions have occurred,” adds co-lead author Blai Vidiella (CNRS).
The paper discusses various mechanisms causing transients, including examples such as coral reef degradation, kelp forests overgrazing, and overexploitation of ocean fish stocks. These real-world instances highlight the challenges ecosystems face and the importance of timely intervention to prevent irreversible damage.
Furthermore, the study emphasizes the importance of incorporating nonlinear dynamics and non-equilibrium phenomena into management and conservation strategies. Ecosystems are complex adaptive systems and their responses to e.g., perturbations, are often highly nonlinear. By understanding the nature of critical transitions through mathematical and computational models, researchers can aid in developing effective conservation policies.
“In our pursuit to prevent ecosystem collapse and promote resilience, it is essential to consider the dynamic nature of ecosystems and the potential for late warning signals,” concludes Sardanyés. “By integrating these concepts into conservation practice, we can enhance our ability to safeguard Earth’s biodiversity for future generations.” The research by Sardanyés, Ivančić and Vidiella presents a significant contribution to conservation biology, offering valuable insights into ecosystem dynamics by integrating theoretical ecology with empirical evidence. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for effective conservation as it allows policymakers and practitioners to anticipate and respond to ecosystem changes, fostering resilience and promoting sustainable management practices.
References: Sardanyés, J., Ivančić, F. and Vidiella, B. (2024), “Identifying regime shifts, transients and late warning signals for proactive ecosystem management”, Biological Conservation, Vol. 290, p. 110433, doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2023.110433.
|
|
CRM CommPau Varela & Mariona Fucho
|
Fuel Cells, Filtration, and Decades of Collaboration: A Conversation with Brian Wetton
Brian Wetton, from the University of British Columbia, spent last October at CRM collaborating with Tim Myers on computational models for filtration systems. His career has evolved from pure numerical analysis to applied mathematics with industrial partners, working...
From Barcelona to West Bengal: Chemistry Meets Mathematics to Enhance Water Filter Design
Researchers at the Centre de Recerca Matemàtica, in collaboration with IIT Kharagpur and UPC, have developed a mathematical model that accurately predicts the performance of fluoride-removal water filters made of mineral-rich carbon (MRC) and...
Polytopes, Matroids, and the Friends You Make: Martina Juhnke on Two Months at the CRM
The Centre de Recerca Matemàtica recently hosted a research programme on Combinatorial Geometries and Geometric Combinatorics, focusing on the overlap between polytopes and matroids. Martina Juhnke, a member of the scientific committee, reflects on how this programme...
BAMB! 2025: Participants Return to the CRM for Research Stays
In October 2025, the Centre de Recerca Matemàtica hosted Josefine Meyer (ISTA) and Cate MacColl (University of Queensland) for a month-long research stay following their participation in the BAMB! Summer School. Despite studying vastly different subjects, from...
Connecting Shapes, Patterns, and Ideas: the Closing Conference on Combinatorial Geometries and Geometric Combinatorics
During five days, the CRM hosted the Closing Conference of the MDM Focused Research Programme on Combinatorial Geometries & Geometric Combinatorics. The event featured plenary talks, contributed sessions, and posters on topics from matroids and polytopes to...
Xavier Ros-Oton among the 65 most cited mathematicians in the world
ICREA professor at the Universitat de Barcelona and CRM affiliated researcher Xavier Ros-Oton appears on Clarivate's Highly Cited Researchers 2025 list, which this year reinstates the mathematics category after two years of exclusion.Citations are a strange way to...
New Horizons for H- and Γ-convergence: From Local to Nonlocal (and viceversa)
The researchers Maicol Caponi, Alessandro Carbotti, and Alberto Maione extended the H- and Γ-convergence theories to the setting of nonlocal linear operators and their corresponding energies. The authors were able to overcome the limitations of classical localization...
Diego Vidaurre joins the CRM through the ATRAE talent programme
Diego Vidaurre has joined the Centre de Recerca Matemàtica through the ATRAE programme, bringing his expertise in modelling spontaneous brain activity across multiple data modalities. His work focuses on understanding how the brain’s intrinsic dynamics shape...
El CRM a la Setmana de la Ciència: una ruta entre dones, formes i pensament
El CRM va participar en la 30a edició de la Setmana de la Ciència amb una ruta guiada que va combinar les biografies de dones matemàtiques amb obres d'art del centre, connectant ciència, història i creació artística.El 12 de novembre, el Centre de Recerca Matemàtica...
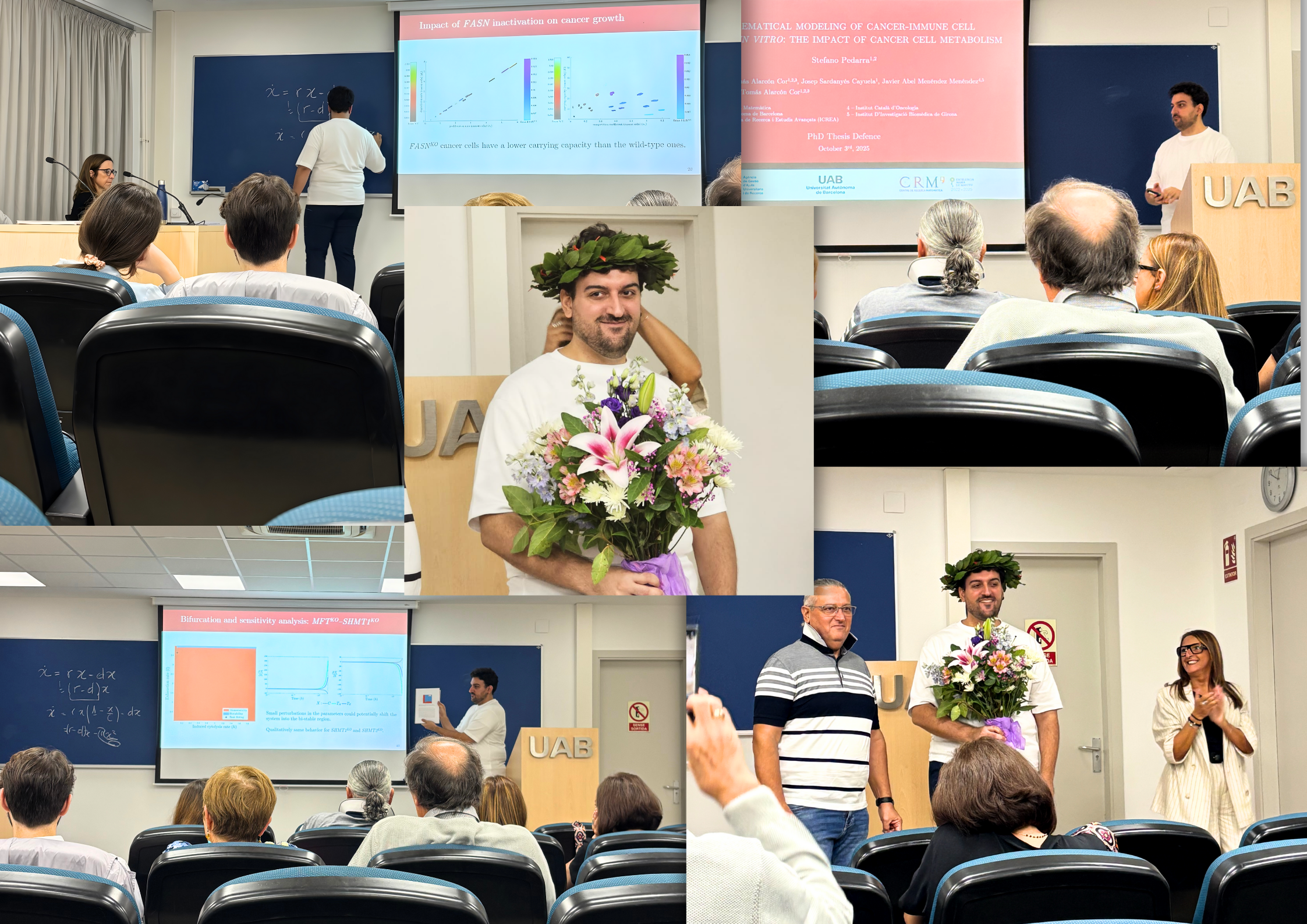
Stefano Pedarra Defends his PhD Thesis on the Interaction between Tumour Cells and the Immune System
Stefano Pedarra has completed his PhD at the Centre de Recerca Matemàtica with a thesis exploring how tumour-cell metabolism shapes the immune system’s ability to fight cancer. His work brought mathematics and biology into direct conversation, from building models to...
Els estudiants participants a la prova de preselecció de Bojos per les Matemàtiques visiten el CRM
La prova de preselecció de Bojos per les Matemàtiques va reunir estudiants de tot Catalunya a la UAB i al CRM, amb presentacions a càrrec de Montse Alsina, presidenta de la Societat Catalana de Matemàtiques, Núria Fagella, degana de la Facultat de Matemàtiques i...
Jordi Mompart highlights the role of artificial intelligence in sport at the XIII GEFENOL-DIFENSC Summer School
The XIII GEFENOL-DIFENSC Summer School gathered over thirty researchers from across Europe to explore how statistical physics helps explain complex phenomena in biology, ecology, networks, and social systems. In his closing lecture, Jordi Mompart (UAB) examined how...